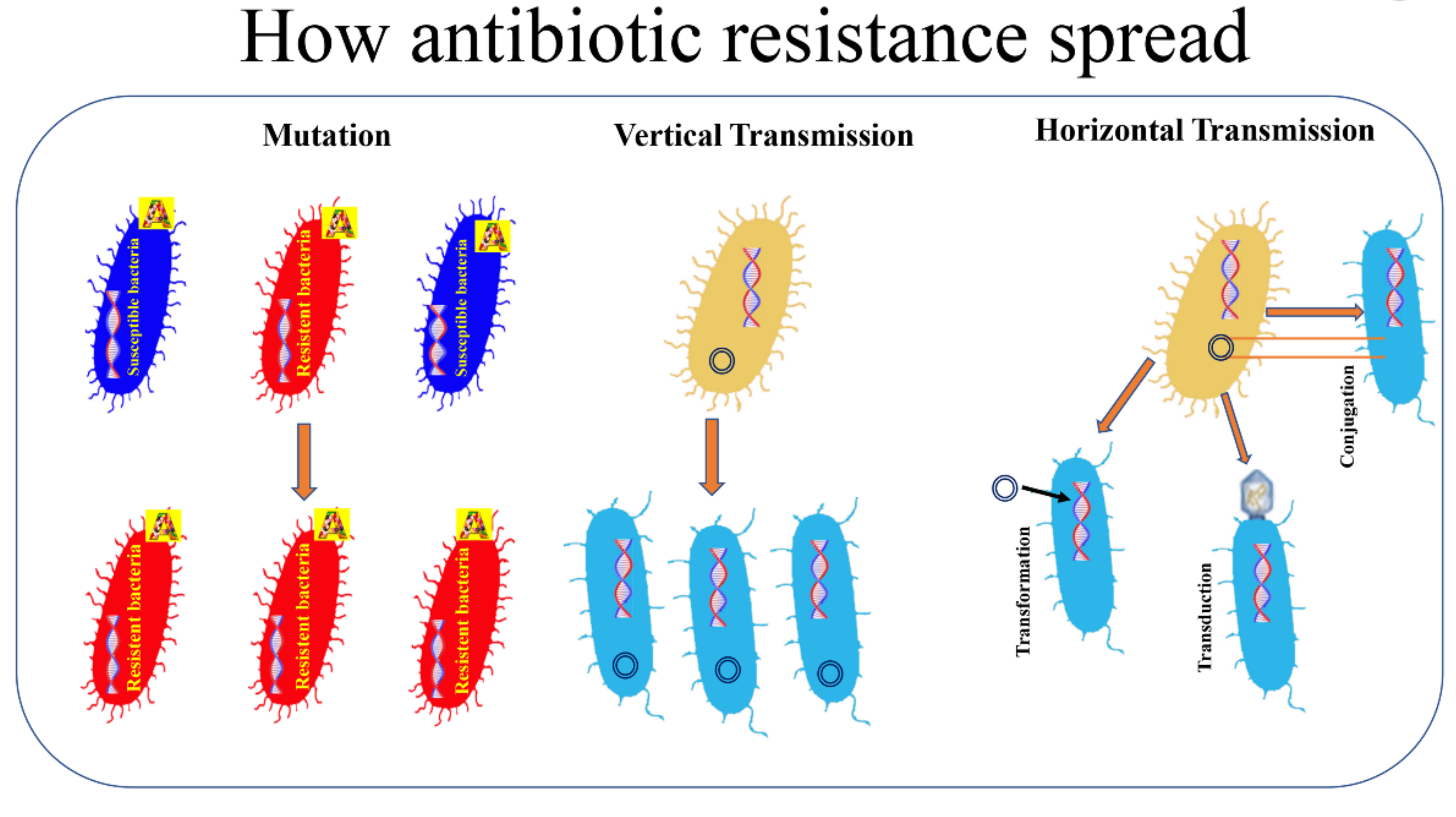
Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens . Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance.
from www.mdpi.com
The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,.
Pathogens Free FullText Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance The Most
Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,.
From www.researchgate.net
Multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index of CES pathogens Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From jama.jamanetwork.com
Antibiotic Resistance Infectious Diseases JAMA JAMA Network Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.mdpi.com
Pathogens Free FullText Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance The Most Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. These pathogens are resistant to. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From saludequitativa.blogspot.com.es
GESTIÓN EN SALUD PÚBLICA Antibiotic Resistance from the Farm to the Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.mdpi.com
Antibiotics Free FullText Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Nickel chelation therapy as an approach to combat multidrug Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.researchgate.net
Antibiotic resistance emergence and selection over bacterial through Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.nature.com
The staggering death toll of drugresistant bacteria Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From theconversation.com
How to train the body's own cells to combat antibiotic resistance Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers In silico analyses of diversity and dissemination of Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From onlinepublichealth.gwu.edu
How Bacteria Build Resistance at the Cellular Level Online Public Health Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From atlasofscience.org
Fecal microbial transplantation a novel approach to eradicate Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. These pathogens are resistant to. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www2.mdpi.com
Antibiotics Free FullText Strategies to Combat MultidrugResistant Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From sparthamedical.eu
Antibiotic resistance SPARTHA Medical Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From thl.fi
Around the world antibioticresistant bacteria are causing increased Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Antimicrobial Resistance in Enteric Pathogens in Developing Countries Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant driver for the persistence and spread of enteric diseases,. The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.nature.com
Molecular Insights into Antimicrobial Resistance Traits of Multidrug Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens Distinct bacterial species that cause enteric disease can exist as invasive enteropathogens that immediately evoke gastrointestinal distress, or. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. These pathogens are resistant to multiple antibiotics and can cause severe and. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.
From www.frontiersin.org
Frontiers Antibiotic Potentiators Against MultidrugResistant Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens The multiple antibiotic resistance ( mar) operon of escherichia coli is a paradigm for chromosomally encoded antibiotic resistance. Predominant enteric bacteria isolates were escherichia coli ( 24, 39.3%), salmonella species ( 12, 19.7%), klebsiella species ( 4,. Antimicrobial resistance is one of the largest threats to global health and imposes. Antimicrobial resistance (amr) has been established to be a significant. Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Enteric Pathogens.